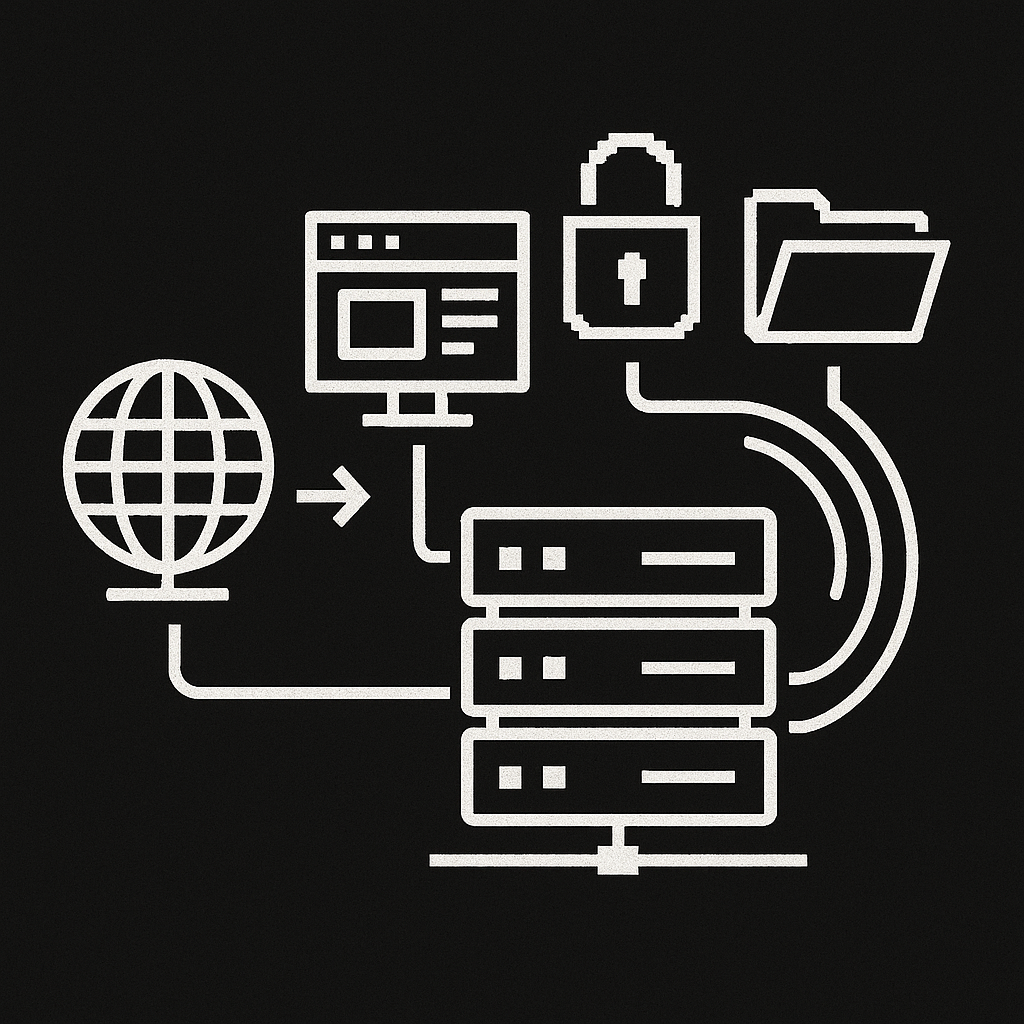
Build, Expose, Route — Effortlessly.
Global installation sets up NetGet system-wide, providing access to its Command Line Interface (CLI) for configuring network routes and exposing services.
Installation:
Compatible with Unix-based systems (Linux, macOS).
npm i -g netgetStart NetGet on your Terminal by running:
netget- Expose your IP securely via HTTPS
- Manage multiple domains and SSL certificates
- Route HTTPS requests to internal services
- Serve static content via HTTPS
- Port management and built-in diagnostics
- Wildcard certificates and subdomain support
When NetGet is installed on your server, it binds to your public IP and starts listening for HTTP and HTTPS traffic.
You use the NetGet CLI to register your domains and subdomains, specifying where each one should route — either to an internal service (via port) or to a static folder.
All incoming requests are:
- Automatically redirected from HTTP to HTTPS for secure connections.
- Matched against the registered domains.
- Routed to the appropriate port or static content you’ve defined.
NetGet also manages your SSL certificates, issuing and renewing them automatically so you don’t have to worry about HTTPS setup.
Suppose you own example.com, and you want to:
- Route https://example.com to a static folder serving a React web interface.
- Point api.example.com to a backend service exposing your API.
With NetGet, you can manage this — and as many domains and subdomains as needed — from a single interface.
Simply point your domain(s) to your server’s IP address, then use the NetGet CLI to:
- Route example.com to your React build directory.
- Forward api.example.com to the port where your API is running.
NetGet will automatically handle SSL certificates for all configured endpoints.
Just ensure your applications are actively running on the ports defined in NetGet — it will take care of the routing, HTTPS encryption, and traffic flow.
NetGet includes a built-in Port Management module to help you monitor, inspect, and free up ports directly from the CLI.
To access:
netgetNavigate to Port Management using the arrow keys.
- Inspect Port: See which process is using a specific port, with PID and service info.
- Kill Process on Port: Free a blocked or stuck port by terminating the process.
Gain full visibility and control over your device’s port allocation and traffic routing.
Whether you're a solo developer or managing infrastructure at scale, NetGet provides a unified way to expose local services, manage traffic, and build modular, decentralized architectures — with ease, flexibility, and security.
Interested in collaborating or improving NetGet? We'd love your input.
License: MIT (see LICENSE)